Labeled:Z9surbj6cs8= Animal Cell
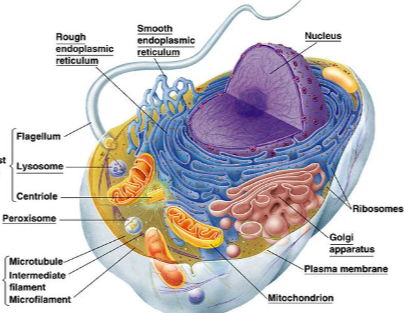
You might not be aware that within the intricate world of a labeled animal cell lies a network of organelles each playing a vital role in maintaining cellular functions. As you explore the depths of this microscopic universe, you will uncover how these organelles work in harmony to ensure the cell’s survival and functionality. From the powerhouse mitochondria to the protein-processing Golgi apparatus, each component contributes to the intricate machinery that keeps the cell operating smoothly. But what secrets do these organelles hold, and how do they collaborate to sustain life within the cell?
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the animal cell. Protein transport plays a crucial role in this process, aiding in the movement of specific molecules across the membrane.
Additionally, cell signaling mechanisms are integral for coordinating cellular activities and responses to external stimuli. Through these intricate processes, the cell membrane maintains the cell’s internal environment while facilitating communication with the external environment.
Read more: Labeled:Z9surbj6cs8= Animal Cell Diagram
Nucleus
The nucleus of an animal cell plays a crucial role in regulating cellular activities. Its structure, which includes a nuclear membrane and nucleoplasm, houses genetic material essential for cell function.
Understanding the nucleus’s importance is key to grasping the complexity of cell biology.
Nucleus Function
Housing the genetic material of the cell, the nucleus directs cellular activities by controlling gene expression. It manages DNA storage, crucial for genetic control, and regulates cell division.
The nucleus acts as the command center, orchestrating processes essential for cell function and growth. Through gene expression, it dictates which proteins are synthesized, influencing the cell’s behavior and characteristics.
This pivotal role makes the nucleus a vital component in maintaining cellular integrity.
Nucleus Structure
Containing a double membrane with pores, the nucleus serves as the central hub for genetic information within the animal cell. It’s the primary site for DNA storage, housing the cell’s genetic material.
Through intricate mechanisms, the nucleus regulates gene expression, controlling which genes are turned on or off. This precise control over gene regulation is crucial for the cell to function properly and respond to its environment effectively.
Nucleus Importance
Playing a critical role in genetic regulation, the nucleus of an animal cell orchestrates the expression of genes to ensure proper cellular functions. Genetic control within the nucleus is crucial for coordinating various cellular activities.
Additionally, the nucleus serves as the hub for information storage and facilitates DNA replication, essential processes for maintaining cell integrity and enabling growth.
Understanding the nucleus’s significance is key to grasping the intricacies of cellular function.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are crucial organelles within animal cells, primarily known for their role in energy production. They play a vital function in ATP synthesis, which is essential for cellular energy transfer and various metabolic processes.
Understanding the intricate processes within mitochondria is fundamental in comprehending the energy dynamics of animal cells.
Energy Production Process
The organelle responsible for energy production in animal cells is the mitochondria. Through cellular respiration, this powerhouse generates ATP, the cell’s energy currency.
The Krebs cycle, part of aerobic respiration, breaks down glucose to produce energy-rich molecules. Subsequently, the electron transport chain utilizes these molecules to generate ATP efficiently.
Mitochondria play a crucial role in energy production, ensuring the cell has the necessary fuel for its functions.
ATP Synthesis Function
During cellular respiration, ATP synthesis occurs within the mitochondria, where energy-rich molecules are efficiently utilized to generate ATP.
The mitochondrial role in ATP synthesis is crucial for providing energy to the cell. Enzyme activity within the mitochondria facilitates the electron transport chain, leading to the production of ATP.
This process is essential for cellular functions, allowing for the conversion of energy into a usable form for various biochemical reactions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum, a network of membranes within the animal cell, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis.
It consists of two types: smooth ER, involved in lipid metabolism, and rough ER, studded with ribosomes facilitating protein production.
Smooth ER synthesizes lipids, while rough ER aids in the modification and folding of proteins before their transport to other cell parts.
The endoplasmic reticulum is vital for cellular functions and maintaining homeostasis.
Golgi Apparatus
Within the animal cell, the Golgi Apparatus processes, modifies, and packages proteins for transport to various cellular destinations.
The Golgi apparatus, through a series of compartments, carries out protein modification by adding specific sugars and other molecules.
It plays a crucial role in vesicle trafficking, sorting proteins into vesicles for delivery to their designated locations within or outside the cell.
Lysosomes
The Golgi Apparatus processes proteins for transport, and now, let’s shift our focus to Lysosomes, membrane-bound organelles containing enzymes for breaking down cellular waste.
Lysosomes play a vital role in the lysosome digestion process, ensuring the recycling of materials within the cell. Additionally, these organelles have a storage function, holding enzymes and waste until needed.
Lysosomes are crucial for maintaining cellular cleanliness and proper functioning.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles act as storage compartments within animal cells, maintaining cell turgor pressure and storing various substances.
These structures control vacuole size regulation to adapt to the cell’s needs.
Vacuole storage plays a crucial role in the cell’s homeostasis, allowing for the containment of nutrients, waste products, and maintaining the cell’s structural integrity.
The dynamic nature of vacuoles permits rapid adjustments in response to changing environmental conditions, ensuring cellular functionality.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes, essential organelles found in animal cells, actively participate in protein synthesis. These small structures, composed of RNA and proteins, read genetic material to assemble amino acids into proteins.
Ribosomes can be free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. During translation, ribosomes decode messenger RNA (mRNA) to create specific proteins according to the genetic instructions carried by the mRNA.
Cytoskeleton
Composed of protein filaments, the cytoskeleton in animal cells provides structural support and facilitates cellular movement and division.
Cytoskeleton organization is crucial for maintaining cell shape and internal organization.
Dynamic cytoskeletal components, such as microtubules and actin filaments, drive cellular movement by enabling organelle transport and cell migration.
During cell division, the cytoskeleton orchestrates the precise separation of chromosomes and the formation of the cleavage furrow, ensuring accurate cell division.
Conclusion
You have explored the intricate machinery of an animal cell, witnessing the essential roles of its organelles in maintaining cellular functions.
Did you know that the average animal cell contains around 1000 mitochondria, highlighting the critical importance of these powerhouses in energy production?
This statistic underscores the remarkable complexity and efficiency of cellular processes, showcasing the remarkable nature of life at the microscopic level.



